Identify objects in color images using RGB![]() The image has three color components represented by Red, Green and Blue. or HSL
The image has three color components represented by Red, Green and Blue. or HSL![]() The image has three color components represented by Hue, Saturation and Luminosity. color components to create a binary mask for later editing, modification and measurement. Color images use three
binary overlays (one for each color band) and combine them using the Boolean operator OR
The image has three color components represented by Hue, Saturation and Luminosity. color components to create a binary mask for later editing, modification and measurement. Color images use three
binary overlays (one for each color band) and combine them using the Boolean operator OR![]() Includes each pixel that either binary image mask includes. to include each pixel that is within all
three ranges.
Includes each pixel that either binary image mask includes. to include each pixel that is within all
three ranges.
When identifying objects in a RGB color image there may be times when the color variation of an object requires such a broad identification range in the RGB mode that unwanted objects or pixels are also identified. This is often the case when lighting is not even across an image, with shadows and highlights causing apparent changes in color of a uniformly colored object, or when a stained thin section has variable thickness making the stained color appear pale in thinly cut areas.
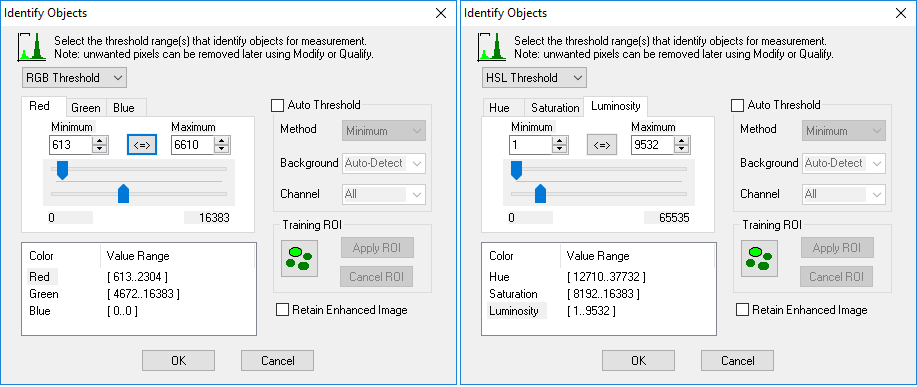
The HSL Transform will create a new image based on the RGB image values where the image has three color components represented by Hue, Saturation and Luminosity.
These transformed image components make it possible to target specific color (Hue) detecting the lighter and darker shades. By selecting a narrow range for the Hue, the exact color is specified; applying broad ranges for the Saturation and Luminosity coordinates will then allow for the variations in the appearance of the color to be detected without including other pure colors.
In both RGB and HSL color space, it is not obvious to humans what the color threshold values might be for any given color tone or color range. To get a first approximation of these color values use the Training ROI button (see "Training ROI (Region of Interest).") to select a portion of the image containing the target color and sample the intensity ranges present for each color component. The sampled values can then be further adjusted if necessary.
Note: While changing color coordinate systems does not affect the appearance of the image, choosing the appropriate color coordinate system (depending on the image data and the goal in mind) can certainly improve the potential for successfully identifying the desired objects via the specification of threshold limits.
The Image Histogram shows the current image intensity distribution with a box outlining the current selected minimum and maximum values. The current values are used for thresholding, and all identified pixels are indicated with brighter colors. Please see "Identify Overview." for more information.